People are living longer. The average mortality rate has gone up by almost twenty years over the last century. Advancement in technology, medical procedures and treatment has made this possible. The need now is to make sure that the quality of life for the aged doesn’t degrade. That is the purpose of geriatric rehabilitation. It offers the aged a means to live a quality life for as long as they can.
How does geriatric rehabilitation help?
Communication, movement and non impairment of mental faculties are what the aged require. As people get old, their hearing and eyesight become impaired. Their movement may get restricted due to wear and tear in the joints, osteoporosis and other age related factors. Another cause for concern for geriatrics is malnutrition. Older people need an excess of certain nutrients to balance their health. Good nutrition promotes healing and provides energy and improves quality of life. Life slows down for the aged, and for the active, this can lead to a feeling of not being a useful contributor to society. This, in turn, can lead to depression. Hence, attending to the mental health of geriatrics is as important as managing physical health.
Different kinds of geriatric rehabilitation
The geriatric rehabilitation includes a wide range of treatments and medical help for a variety of ailments that the aged face.
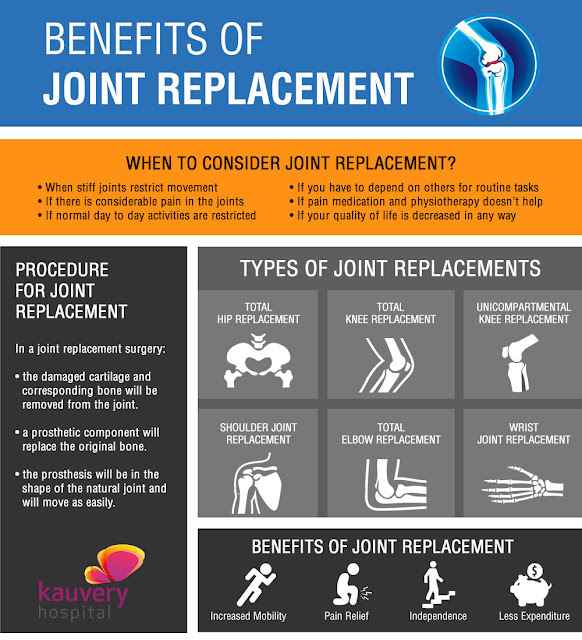
1. One of the major problems that geriatrics deal with is decrease in movement. Earlier, stiffness in the joints, and aches and pains were taken as part and parcel of getting old. But these days, with joint replacement procedures, and physical therapy the aged can get past these problems.
2. Loss of hearing and vision can be addressed these days with simple procedures like laser treatment, advanced hearing aids etc., that help restore or at least better eyesight and hearing.
3. There are specialized dieticians for geriatrics who will prescribe a food plan that includes foods and supplements to ensure that they are getting all the nutrients their body requires.
4. As a person ages, small activities like eating or bathing become difficult. Occupational therapy focuses on helping the aged stay independent. The goal is to help them learn to help themselves.
5. The awareness among doctors and the aged that geriatric mental health needs to be addressed is a boon to the aged. Counselling is available for older people and this can help them adjust to a difference in lifestyle.
Focused geriatric attention
Many hospitals have geriatric departments which focus completely on geriatric health and rehabilitation. They take a holistic approach to the health and wellness of the aged. They have regular medical check-ups for older people and a complete and comprehensive battery of tests that will keep an eye on the person’s health so that preventive action can be taken at the first sign of an illness. This is a boon to the patients as they can live their life comfortably in the knowledge that their health is in safe hands.